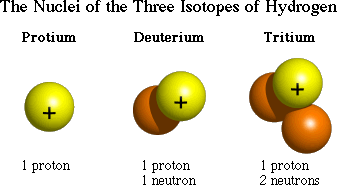
A last definition we need is an isotope:
a form of an element that has a different
number of neutrons.
Remember that the thing that defines an element's
identity is its number of protons.
Most atoms have about the same number
of neutrons in the nucleus
as the number of protons, but not all.
The simplest example is the three isotopes
of hydrogen:

Another famous isotope is carbon-14.
How many protons and neutrons does 14C have?
How many protons and neutrons does
the "normal" form of carbon have?
Some elements have non-radioactive "normal"
forms and radioactive isotopes like carbon
does. Another one you will see in your
homework is aluminum. The stable,
non-radioactive form of aluminum is 27Al.
26Al is a minority isotope that (it turns
out) is radioactive.