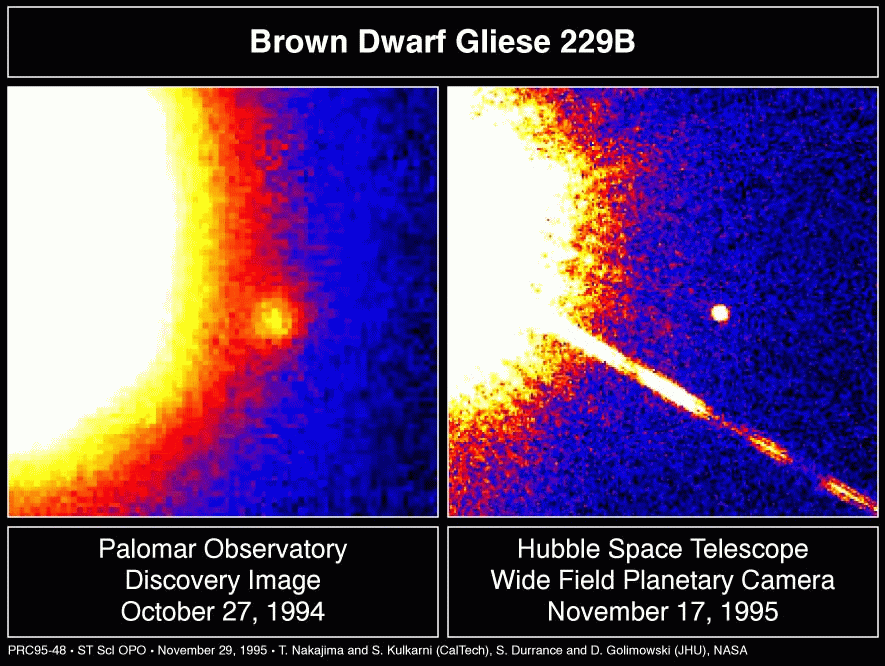
Left: Discovery image of the first confirmed brown dwarf (GL 299B). Right: Hubble Space Telescope image of the same target.
A new kind of star-like object has been discovered in only the last ten years.
Recall that stars form from clouds of gas and dust. These clumps eventually contract and heat up enough in their cores to burn hydrogen, thus becoming stars. What would happen if a protostar formed but without enough mass to raise the temperature to the critical point for hydrogen fusion?
The result is something called a brown dwarf, an object that forms as a star but lacks enough mass to ignite its hydrogen fuel. These were predicted in the early 1960s but were not confirmed to exist until the 1990s. Why is this so?

Left: Discovery image of the first confirmed brown dwarf (GL 299B). Right: Hubble Space Telescope image of the same target.