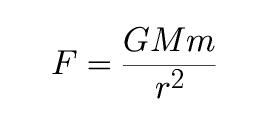
Equation 4
Newton also proposed what is now known as the
Universal Law of Gravitation, which
said that two bodies attract each other
with a force that we now call gravity:
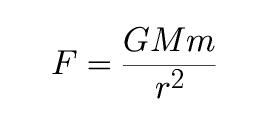
G is the same as before -- the Universal
Gravitation Constant;
M is the mass (kg) of the first body;
m is the mass (kg) of the second body;
and
r is the distance (meters) between the center
of mass of body 1 and the center of mass of body 2.
F here is the force (metric unit: Newtons)
of gravity.
You can see that the force
of gravity goes is big when the masses
are big and small when both masses
are small. You can also see that the
force of gravity is big when the distance
(r) between the masses is small,
and the force of gravity is small when
the distance between the two masses is big.
You will get a chance to practice with the
Universal Law of Gravitation on your homework.